
If no valid breakpoints are set, the debugger executes the whole routine. You can read more about Oracle debugging commands in the official Oracle documentation. You cannot pause the target session or manage breakpoints but you might experience a boost in performance in CPU-intensive operations (operations that include a lot of computations and loops). In Native mode, the debugger uses Oracle native debugging commands.
#DATAGRIP EXECUTION PLAN CODE#
If no valid breakpoints are set, the debugger steps through code on a line-by-line basis. In Graceful mode, you can pause the session that you debug (the target session), set and remove breakpoints. When you debug PL/SQL code, you can select between two stepping modes: Graceful and Native. For this purpose, you can use the Run menu commands, or the icons on the stepping toolbar of in the Debug tool window.Įach stepping action advances the execution point to the next execution location, depending on the action you choose. When a breakpoint is reached, the Debug tool window becomes active and enables you to get control over the program's execution. You can configure whether you want Run to Cursor to work on clicking a line number in Settings | Tools | Debugger. Place the caret at the line where you want the program to pause.Ĭlick the Run to Cursor button or press Alt+F9.Īlso, you can Run to Cursor by clicking the line number in the gutter. Run to cursorĬontinues the execution until the position of the caret is reached. In the example, stepping out skips all iterations of the loop and takes you straight to the main method (the caller). Steps out of the current method and takes you to the caller method.Ĭlick the Step Out button or press Shift+F8. This is done in Settings | Tools | Debugger | Stepping. You can configure Smart Step Into to be used instead of the regular Step Into every time there are multiple method calls on the line. You can also select it using the arrow keys or tabs and press Enter/ F7. This feature allows you to select the method call you are interested in.įrom the main menu, select Run | Debugging Actions | Smart Step Into or press Shift+F7.Ĭlick the method. Smart step into is helpful when there are several method calls on a line, and you want to be specific about which method to enter. If there are several method calls on the line, DataGrip asks you which method to enter. Use this option when you are not sure the method is returning a correct result.
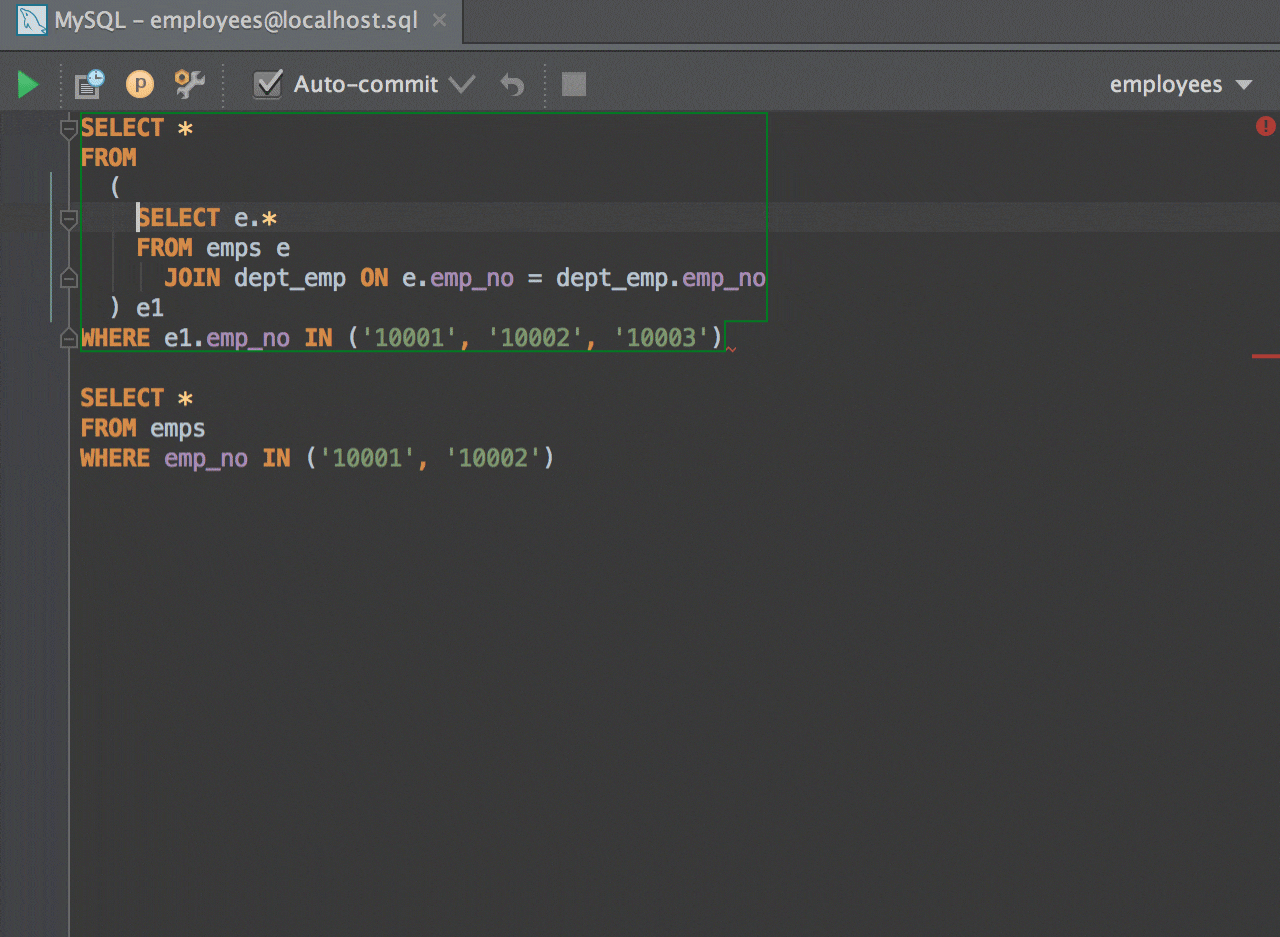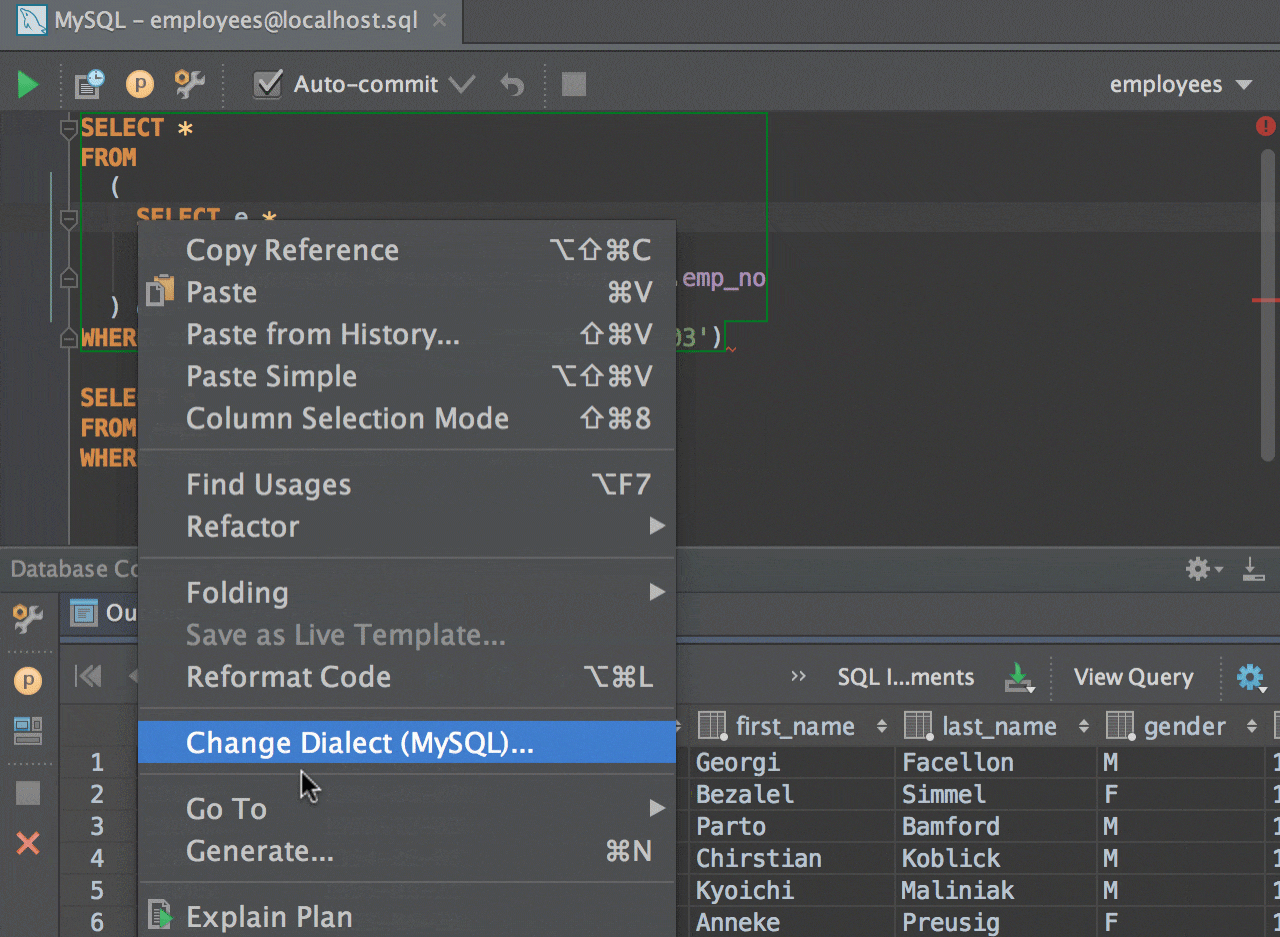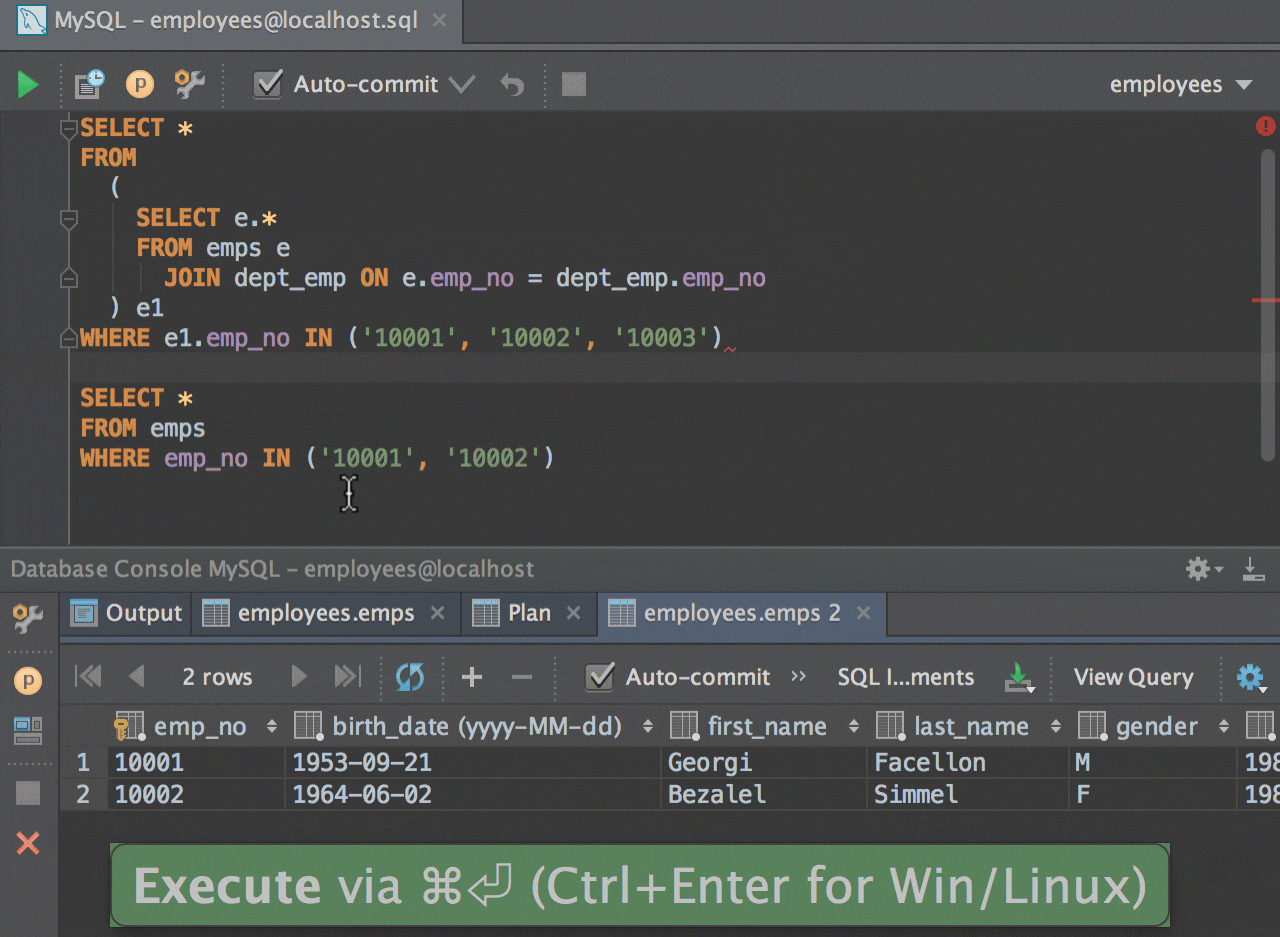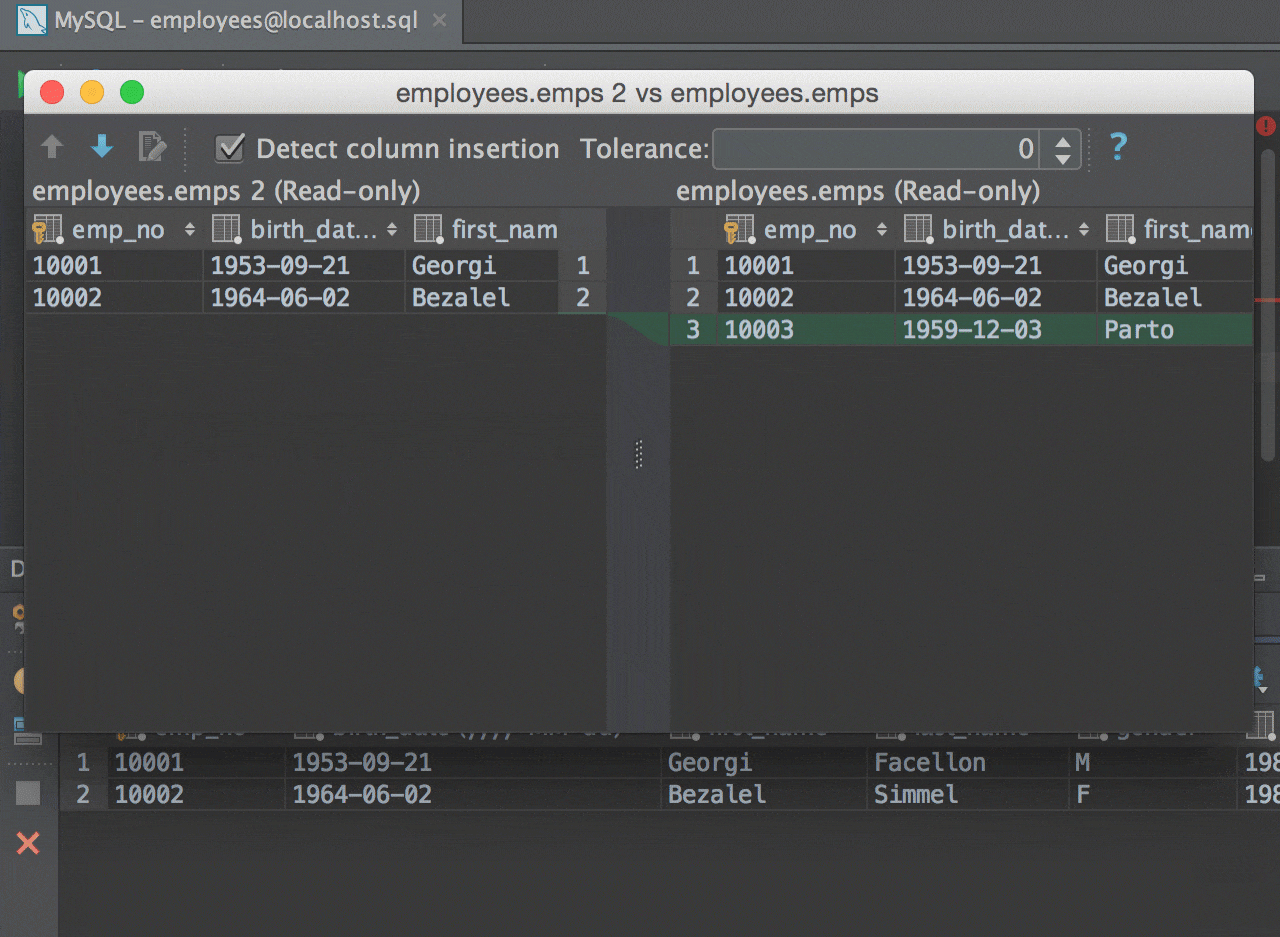
Steps into the method to show what happens inside it. The implementation of the methods is skipped, and you move straight to the next line of the caller method. Steps over the current line of code and takes you to the next line even if the highlighted line has method calls in it. The stepping buttons are located on the Debug window toolbar.
Stepping is the process of controlling step-by-step execution of the program.ĭataGrip provides a set of stepping actions, which are used depending on your strategy (for example, whether you need to go directly to the next line or enter the methods invoked on your way there). Debug functionality is only supported for Oracle databases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
